Autonomous Agents
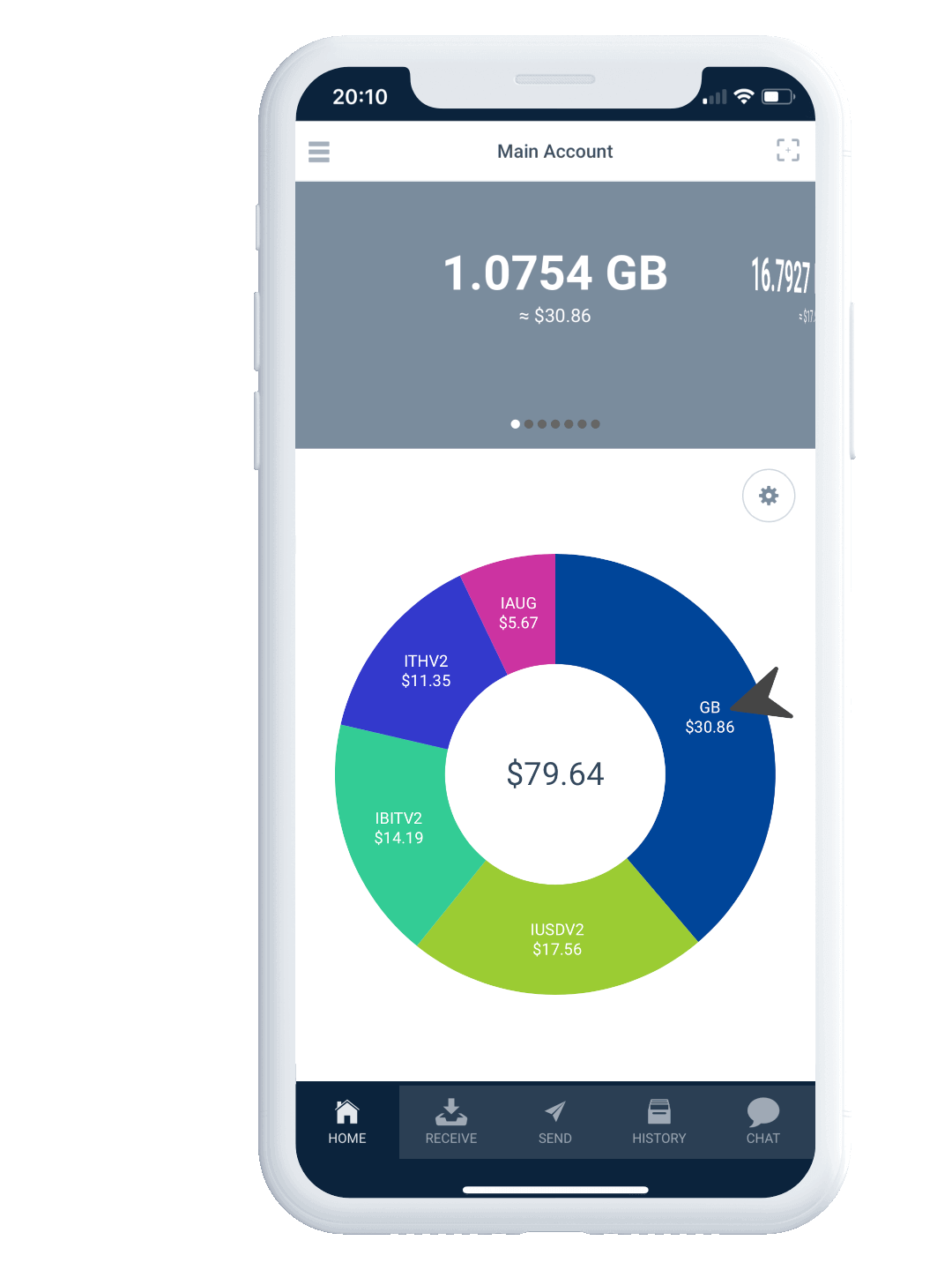
Autonomous Agents are programs that run on the DAG and allow to orchestrate a programmed, strictly rules-based flow and custody of assets, free from any human intervention.
AAs are most useful for creating decentralized finance (DeFi) apps where complete certainty about their performance is of utmost importance.
Decentralized applications (dApps) that can be powered by AAs include:
- tradable shares in prediction markets;
- futures contracts;
- algorithmic stable coins;
- synthetic assets;
- other derivatives;
- collateralized lending;
- margin trading.
Why DAG matters
Unlike blockchains, there are no miners or other intermediaries on DAG, therefore there is no room for miner manipulation. One doesn't need to bother about front-running or censorship by miners. Therefore, dApps running on a DAG are safer than dApps on a blockchain.
How Autonomous Agents work
Autonomous Agents are similar to vending machines. One sends a transaction with some money and data to an AA and expects a response: some other monetary token and some data permanently recorded on the DAG — similar to inserting coins into a vending machine, entering the number of the desired drink on a keypad, and getting the drink in response.
Agents, not contracts
Autonomous Agents are economic agents when dealing with anything of value and they exist on equal terms with human actors: both are endpoints of interactions. Contracts, on the other hand, exist between humans or human-managed organizations, contracts are interactions.

Unlike humans though, AAs are governed by immutable code, not by free will.
Transparency
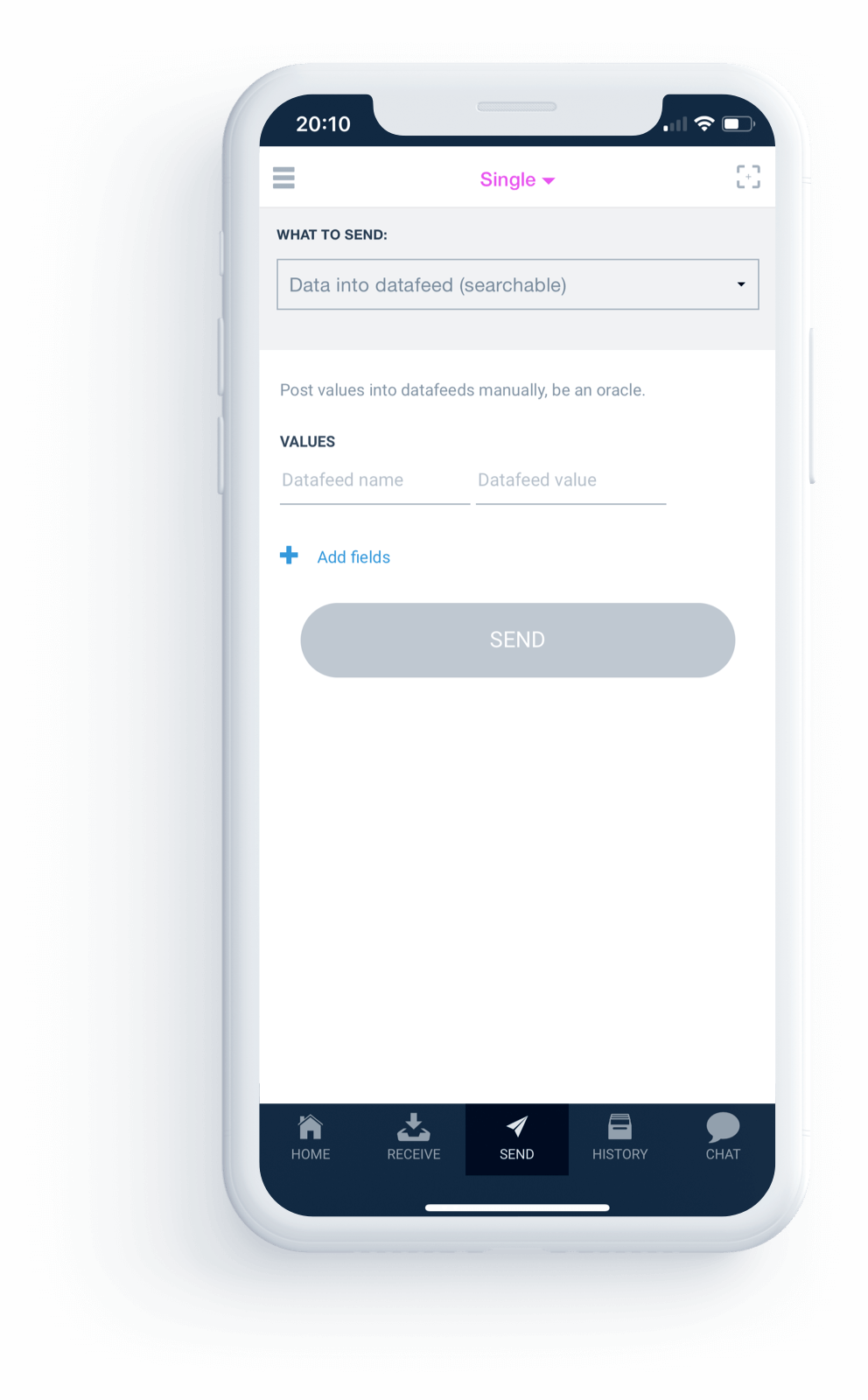
Before actually sending any money or command to an AA, one can see the expected response of the AA.
Developers
Build your AAs
AAs are written in Oscript — a new programming language designed for this purpose.
Oscript avoids some unsafe programming patterns common in earlier languages such as Solidity.
It is easier to see what an AA is going to do, it is harder to make mistakes that would cost millions.
Programming in Oscript is safer. Oscript syntax is easy to learn and will look familiar to those
developers who have experience in JavaScript, PHP, Java, and SQL.
Developer tools
-
Oscript Editor: a browser based editor for Oscript, it allows
to write AA code in the browser, no installation required, and immediately deploy using Obyte wallet.
The editor includes a few templates of AAs to start with.
-
Visual Studio Code plugin for Oscript
also allows to edit and deploy, plus it includes a testkit for running tests.
-
AA Testkit
for running tests and making sure your AA operates correctly in various scenarios of its usage.
See the full developer documentation about Autonomous Agents.
Try AAs now
Some existing AAs: